- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
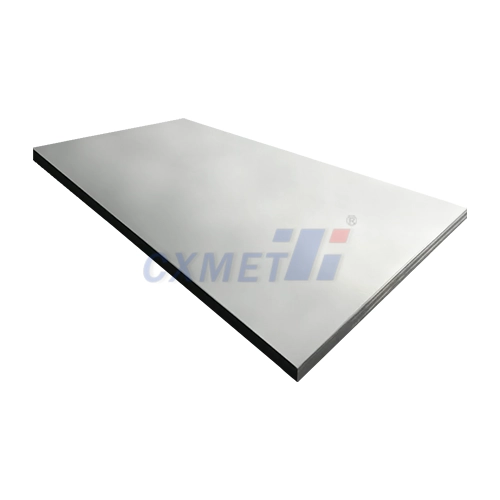
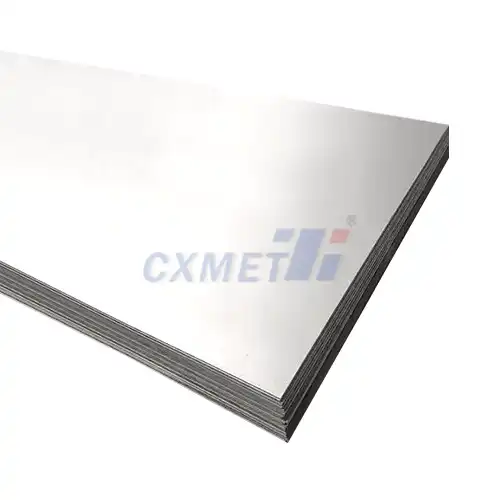
What Is Pure Nickel Sheet And What Are Its Uses?
2025-03-04 11:28:40
Pure nickel sheet is a versatile and highly sought-after material in various industries due to its unique properties and wide range of applications. This thin, flat form of nickel metal is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high melting point, and good electrical and thermal conductivity. Pure nickel sheets are typically composed of at least 99% nickel, with minimal impurities, making them ideal for numerous industrial and technological applications.
|
|
|
How is pure nickel sheet manufactured?
The manufacturing process of pure nickel sheets involves several steps to ensure the highest quality and purity of the final product. The process typically begins with the extraction of nickel from ore through mining operations. Once the raw nickel is obtained, it undergoes a series of refining processes to remove impurities and achieve the desired level of purity, usually 99% or higher.
The refined nickel is then melted and cast into ingots or continuous cast strips. These initial forms are subsequently processed through various metalworking techniques to produce the desired sheet thickness and properties. Some of the common methods used in the production of pure nickel sheets include:
- Hot rolling: The nickel ingots or strips are heated to high temperatures and passed through a series of rollers to reduce their thickness and increase their length. This process helps to improve the material's strength and ductility.
- Cold rolling: After hot rolling, the nickel sheets undergo further rolling at room temperature to achieve the final desired thickness and surface finish. Cold rolling also enhances the material's mechanical properties and provides a smoother surface.
- Annealing: This heat treatment process is often performed between or after rolling operations to relieve internal stresses, improve ductility, and ensure uniformity in the material's properties.
- Surface finishing: Depending on the intended application, pure nickel sheets may undergo additional surface treatments such as polishing, brushing, or chemical cleaning to achieve specific surface characteristics.
The manufacturing process is carefully controlled to maintain the purity of the nickel and ensure consistent quality throughout the sheet. Advanced quality control measures, including chemical analysis, mechanical testing, and surface inspection, are employed to verify that the final product meets the required specifications.
Pure nickel sheets are available in various grades, thicknesses, and dimensions to suit different applications. Common grades include Nickel 200 and Nickel 201, which offer slightly different compositions and properties to cater to specific industry needs. The thickness of pure nickel sheets can range from ultra-thin foils (less than 0.025 mm) to thicker plates (several millimeters), allowing for versatility in their use across various industries.
What are the key properties of pure nickel sheets?
Pure nickel sheets possess a unique combination of properties that make them valuable in numerous applications across various industries. Understanding these key properties is essential for engineers, designers, and manufacturers when selecting materials for specific projects. Here are the main characteristics of pure nickel sheets:
- Excellent corrosion resistance: Pure nickel sheets exhibit outstanding resistance to corrosion in various environments, including atmospheric conditions, seawater, and many alkaline and organic compounds. This property makes them ideal for use in chemical processing equipment, marine applications, and food processing machinery.
- High melting point: With a melting point of approximately 1,455°C (2,651°F), pure nickel sheets can withstand high temperatures without losing their structural integrity. This characteristic is crucial in applications involving heat exchangers, furnace components, and high-temperature processing equipment.
- Good electrical conductivity: Although not as conductive as copper or silver, pure nickel sheets offer reliable electrical conductivity. This property makes them suitable for use in electrical contacts, battery electrodes, and other electronic components.
- Thermal conductivity: Pure nickel sheets possess moderate thermal conductivity, allowing for efficient heat transfer in various applications. This property is particularly useful in heat exchangers and thermal management systems.
- Magnetic properties: Pure nickel is ferromagnetic at room temperature, meaning it can be magnetized and attracted to magnets. This property is exploited in applications such as magnetic shielding and electromagnetic components.
- Ductility and malleability: Pure nickel sheets are highly ductile and malleable, allowing them to be easily formed, bent, and shaped into various configurations without breaking. This characteristic is valuable in manufacturing processes that require complex shapes or deep drawing.
- Strength and hardness: While not as strong as some alloys, pure nickel sheets offer good mechanical strength and hardness, making them suitable for structural applications in corrosive environments where other materials might fail.
- Low gas permeability: Pure nickel sheets have low gas permeability, making them effective barriers against gas diffusion. This property is utilized in vacuum technology and gas containment applications.
- Catalytic activity: Nickel has catalytic properties that make it useful in certain chemical reactions. Pure nickel sheets can be used as catalysts or catalyst supports in various industrial processes.
- Non-magnetic at high temperatures: Although ferromagnetic at room temperature, pure nickel becomes non-magnetic at its Curie point (approximately 354°C or 669°F). This property is exploited in specialized applications where magnetic properties need to be controlled with temperature.
These properties, combined with nickel's relatively good workability and weldability, make pure nickel sheets a versatile material for a wide range of industrial applications. The specific combination of these properties often makes pure nickel the material of choice in situations where other metals or alloys might fall short in performance or durability.
|
|
|
Where are pure nickel sheets commonly used in industry?
Pure nickel sheets find extensive use across various industries due to their unique combination of properties. Their versatility and reliability make them indispensable in many critical applications. Here are some of the key industries and applications where pure nickel sheets are commonly used:
- Chemical Processing Industry:
- Reaction vessels and tanks for corrosive chemicals
- Heat exchangers in chemical plants
- Piping and valves for aggressive media
- Catalyst supports for chemical reactions
- Electronics and Electrical Industry:
- Battery electrodes, particularly in nickel-cadmium and nickel-metal hydride batteries
- Electrical contacts and connectors
- Electromagnetic shielding components
- Spark plug electrodes
- Aerospace and Defense:
- Components for jet engines
- Missile and rocket parts
- Honeycomb structures for aircraft
- Radar and communication equipment
- Energy Sector:
- Solar panel components
- Fuel cell electrodes
- Nuclear reactor components
- Heat exchangers in power plants
- Automotive Industry:
- Catalytic converters
- Fuel system components
- Electrical connectors in harsh environments
- Specialized engine parts
- Food Processing and Pharmaceutical Industries:
- Process equipment and vessels
- Mixing tanks and reactors
- Filtration systems
- Sterilization equipment
- Marine and Offshore Applications:
- Shipbuilding components
- Desalination plant equipment
- Offshore oil and gas platform components
- Submarine cable sheathing
- Scientific Research and Laboratory Equipment:
- Vacuum chambers and seals
- Cryogenic vessels
- Specialized research instruments
- Electron microscope components
- Plating and Surface Finishing:
- Electroplating anodes
- Base material for specialized coatings
- Decorative applications
- Hydrogen Production and Storage:
- Electrolyzers for hydrogen production
- Hydrogen storage tanks and components
- Fuel cell components
The use of pure nickel sheets in these industries is driven by their ability to withstand corrosive environments, high temperatures, and mechanical stress while maintaining their structural integrity and functionality. In many cases, pure nickel sheets are chosen over other materials due to their longer service life, reduced maintenance requirements, and overall cost-effectiveness in challenging applications.
As technology advances and new industries emerge, the applications for pure nickel sheets continue to expand. For example, in the growing field of renewable energy, pure nickel sheets are finding new uses in advanced battery technologies, hydrogen fuel cells, and solar energy systems. Additionally, the increasing focus on sustainability and environmental protection has led to the use of pure nickel sheets in pollution control equipment and eco-friendly manufacturing processes.
The versatility of pure nickel sheets also allows for customization to meet specific industry needs. Manufacturers can produce sheets with varying thicknesses, surface finishes, and dimensions to suit particular applications. This flexibility, combined with nickel's inherent properties, ensures that pure nickel sheets will remain a crucial material in industrial applications for years to come.
At SHAANXI CXMET TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD, we take pride in our extensive product range, which caters to diverse customer needs. Our company is equipped with outstanding production and processing capabilities, ensuring the high quality and precision of our products. We are committed to innovation and continuously strive to develop new products, keeping us at the forefront of our industry. With leading technological development capabilities, we are able to adapt and evolve in a rapidly changing market. Furthermore, we offer customized solutions to meet the specific requirements of our clients. If you are interested in our products or wish to learn more about the intricate details of our offerings, please do not hesitate to contact us at sales@cxmet.com. Our team is always ready to assist you.
|
|
|
|
References
- Nickel Institute. (2021). Nickel in Manufacturing.
- ASM International. (2000). ASM Specialty Handbook: Nickel, Cobalt, and Their Alloys. Materials Park, OH: ASM International.
- Crundwell, F. K., et al. (2011). Extractive Metallurgy of Nickel, Cobalt and Platinum Group Metals. Elsevier.
- Davis, J. R. (Ed.). (2000). Nickel, Cobalt, and Their Alloys. ASM International.
- Special Metals Corporation. (2021). Nickel 200 & 201 Technical Data.
- Mond, L., Langer, C., & Quincke, F. (1890). Action of carbon monoxide on nickel. Journal of the Chemical Society, Transactions, 57, 749-753.
- Agarwal, D. C. (1996). Nickel and nickel alloys. In Uhlig's Corrosion Handbook (Vol. 3). John Wiley & Sons.
- Mankins, W. L., & Lamb, S. (1990). Nickel and nickel alloys. Properties and Selection: Nonferrous Alloys and Special-Purpose Materials, 2, 428-445.
- International Nickel Study Group. (2021). World Nickel Statistics.
- Reck, B. K., & Graedel, T. E. (2012). Challenges in metal recycling. Science, 337(6095), 690-695.