- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
How does Grade 5 of Titanium 6Al-4V Differ From Other Grades?
Titanium 6Al-4V Grade 5 is a widely recognized and extensively used titanium alloy, renowned for its exceptional combination of strength, lightweight properties, and corrosion resistance. This particular grade stands out among other titanium grades due to its unique composition and superior mechanical characteristics. Grade 5 titanium, also known as Ti-6Al-4V, contains 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium, which contribute to its enhanced properties compared to other grades. This alloy's distinctive features make it a preferred choice in various high-performance applications across multiple industries.
What are the key properties of Titanium 6Al-4V Grade 5 Sheet?
Titanium 6Al-4V Grade 5 sheet exhibits a remarkable set of properties that set it apart from other materials and even other titanium grades. Its high strength-to-weight ratio is one of its most notable characteristics, making it an ideal choice for applications where weight reduction is crucial without compromising structural integrity. This alloy typically has a tensile strength ranging from 895 to 1000 MPa, which is significantly higher than many other metals and titanium grades.
Corrosion resistance is another standout property of Grade 5 titanium. The alloy forms a stable, continuous, tightly adhering oxide film on its surface when exposed to oxygen, providing excellent protection against various corrosive environments. This natural passivation layer makes Grade 5 titanium highly resistant to saltwater, marine atmospheres, and many industrial chemicals, outperforming stainless steel in numerous corrosive settings.
The material's fatigue strength is also noteworthy, allowing it to withstand cyclic loading conditions better than many other metals. This property is particularly valuable in aerospace and automotive applications where components are subjected to repeated stress cycles. Grade 5 titanium's fatigue limit is typically around 510 MPa for 10^7 cycles, which is impressive compared to other structural materials.
Temperature performance is another area where Titanium 6Al-4V Grade 5 sheet excels. It maintains its strength and structural integrity over a wide temperature range, from cryogenic temperatures up to about 400°C (752°F). This temperature stability makes it suitable for applications in both extremely cold environments and moderately high-temperature settings.
The alloy's biocompatibility is a crucial property that has led to its widespread use in medical implants and surgical instruments. The human body tolerates titanium exceptionally well, with minimal risk of allergic reactions or rejections. This compatibility, combined with its strength and corrosion resistance, makes Grade 5 titanium an excellent choice for long-term implants such as joint replacements and dental implants.
Lastly, the machinability of Titanium 6Al-4V Grade 5 sheet, while challenging compared to some other metals, is generally better than other titanium alloys. With proper tooling and techniques, it can be machined, welded, and formed into complex shapes, allowing for versatile manufacturing processes and design possibilities.
How does Titanium 6Al-4V Grade 5 compare to other titanium grades?
When comparing Titanium 6Al-4V Grade 5 to other titanium grades, several key differences become apparent. Grade 5 is classified as an alpha-beta alloy, which means it contains both alpha and beta phase microstructures. This dual-phase composition contributes to its superior strength and heat-treatability compared to single-phase titanium alloys.
Commercially pure (CP) titanium grades, such as Grade 1, 2, 3, and 4, offer excellent corrosion resistance and formability but lack the strength of Grade 5. For instance, Grade 2 titanium, which is widely used in chemical processing equipment, has a typical yield strength of about 275-450 MPa, significantly lower than Grade 5's 825-910 MPa. This strength difference makes Grade 5 more suitable for applications requiring high strength-to-weight ratios, such as aerospace components.
Grade 23, also known as Ti-6Al-4V ELI (Extra Low Interstitial), is a variant of Grade 5 with lower oxygen content. While it shares many properties with Grade 5, it offers improved ductility and fracture toughness, making it particularly suitable for cryogenic applications and medical implants. However, Grade 23's yield strength is slightly lower than Grade 5, typically ranging from 760-827 MPa.
Beta titanium alloys, such as Ti-15V-3Cr-3Al-3Sn (Ti-15-3-3-3), offer higher strength and better formability at room temperature compared to Grade 5. However, they are generally more expensive and may not provide the same level of elevated temperature performance as Grade 5.
Grade 7 and Grade 11 titanium, which contain small amounts of palladium, offer superior corrosion resistance in reducing acid environments compared to Grade 5. However, they lack the strength of Grade 5 and are primarily used in specific chemical processing applications where extreme corrosion resistance is required.
In terms of weldability, Grade 5 performs well but requires careful control of welding parameters to avoid embrittlement. Some other grades, like CP titanium, are generally easier to weld but cannot match Grade 5's strength.
The heat treatability of Grade 5 is superior to many other titanium grades. It can be solution treated and aged to achieve a wide range of strength levels, allowing for tailored properties to suit specific applications. This versatility in heat treatment is not available with CP titanium grades or some other alpha alloys.
What are the primary applications for Titanium 6Al-4V Grade 5 Sheet?
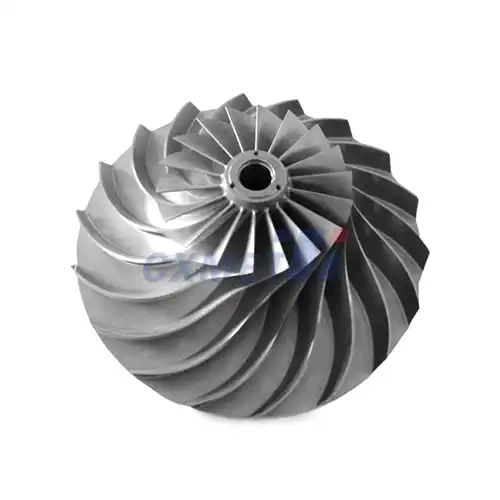
Titanium 6Al-4V Grade 5 sheet finds extensive use across various industries due to its exceptional combination of properties. In the aerospace sector, it's a crucial material for aircraft structural components, engine parts, and spacecraft. Its high strength-to-weight ratio allows for significant weight reduction in aircraft, improving fuel efficiency and performance. Specific applications include fuselage frames, engine cases, landing gear components, and fasteners.
The medical industry heavily relies on Grade 5 titanium for implants and surgical instruments. Its biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and strength make it ideal for hip and knee replacements, dental implants, bone plates, and screws. The material's ability to osseointegrate – allowing bone to grow and adhere directly to its surface – is particularly valuable in orthopedic and dental applications.
In the automotive industry, Grade 5 titanium is used in high-performance vehicles for components like connecting rods, valves, and exhaust systems. Its high strength and heat resistance make it suitable for these demanding applications, where weight reduction and performance are critical.
The marine industry utilizes Grade 5 titanium for its excellent corrosion resistance in saltwater environments. It's used in propeller shafts, underwater robotics, and various components in offshore oil and gas extraction equipment.
In chemical processing, while not as commonly used as CP titanium grades, Grade 5 finds applications where higher strength is required alongside corrosion resistance. It's used in pressure vessels, heat exchangers, and reactor components in aggressive chemical environments.
The sports equipment industry also benefits from Grade 5 titanium's properties. It's used in golf club heads, bicycle frames, and other high-performance sporting goods where strength, lightweight, and durability are essential.
Lastly, the aerospace and defense sectors employ Grade 5 titanium in missile components, armor plating, and various military hardware. Its high ballistic performance-to-weight ratio makes it valuable in protective applications.
At SHAANXI CXMET TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD, we take pride in our extensive product range, which caters to diverse customer needs. Our company is equipped with outstanding production and processing capabilities, ensuring the high quality and precision of our products. We are committed to innovation and continuously strive to develop new products, keeping us at the forefront of our industry. With leading technological development capabilities, we are able to adapt and evolve in a rapidly changing market. Furthermore, we offer customized solutions to meet the specific requirements of our clients. If you are interested in our products or wish to learn more about the intricate details of our offerings, please do not hesitate to contact us at sales@cxmet.com. Our team is always ready to assist you.
References:
1. ASM International. (2015). Titanium: A Technical Guide. Materials Park, OH: ASM International.
2. Leyens, C., & Peters, M. (Eds.). (2003). Titanium and Titanium Alloys: Fundamentals and Applications. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH.
3. Boyer, R., Welsch, G., & Collings, E. W. (1994). Materials Properties Handbook: Titanium Alloys. Materials Park, OH: ASM International.
4. Donachie, M. J. (2000). Titanium: A Technical Guide (2nd ed.). Materials Park, OH: ASM International.
5. Peters, M., Kumpfert, J., Ward, C. H., & Leyens, C. (2003). Titanium Alloys for Aerospace Applications. Advanced Engineering Materials, 5(6), 419-427.
6. Rack, H. J., & Qazi, J. I. (2006). Titanium alloys for biomedical applications. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 26(8), 1269-1277.
7. Lütjering, G., & Williams, J. C. (2007). Titanium (2nd ed.). Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
8. Froes, F. H. (Ed.). (2015). Titanium: Physical Metallurgy, Processing, and Applications. Materials Park, OH: ASM International.
9. Banerjee, D., & Williams, J. C. (2013). Perspectives on Titanium Science and Technology. Acta Materialia, 61(3), 844-879.
10. Boyer, R. R. (1996). An overview on the use of titanium in the aerospace industry. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 213(1-2), 103-114.
 titanium wire 1.webp)